Highlights
White Collar Exemptions Apply to:
- Executive, administrative and professional employees
- Outside sales personnel
- Certain computer employees
- Certain highly compensated employees
Qualifications
To qualify for a white collar exemption, an employee must meet:
- A salary basis test;
- A salary level test; and
- A duties test.
Links And Resources
- DOL Fair Labor Standards Act Advisor
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) regulates minimum wage and overtime payment provisions for employees. Most employers and employees in the United States are subject to the FLSA.
Among other things, the FLSA requires employers to compensate their employees for all hours employees are “suffered or permitted” to work. This means that an employer must compensate its employees for all hours employees actually work and all hours during which employees are required to remain available for their next assignment.
However, the FLSA also provides various exemptions from minimum wage and overtime payment provisions. Among these, the most common are the “white collar” exemptions. The white collar exemptions apply mainly to executive, administrative and professional (EAP) employees, but they also include outside sales personnel and certain computer and highly compensated employees.
This Compliance Overview provides an overview of the white collar exemptions, as well as an overview of the requirements employees must meet to qualify for them.
The White Collar Exemptions
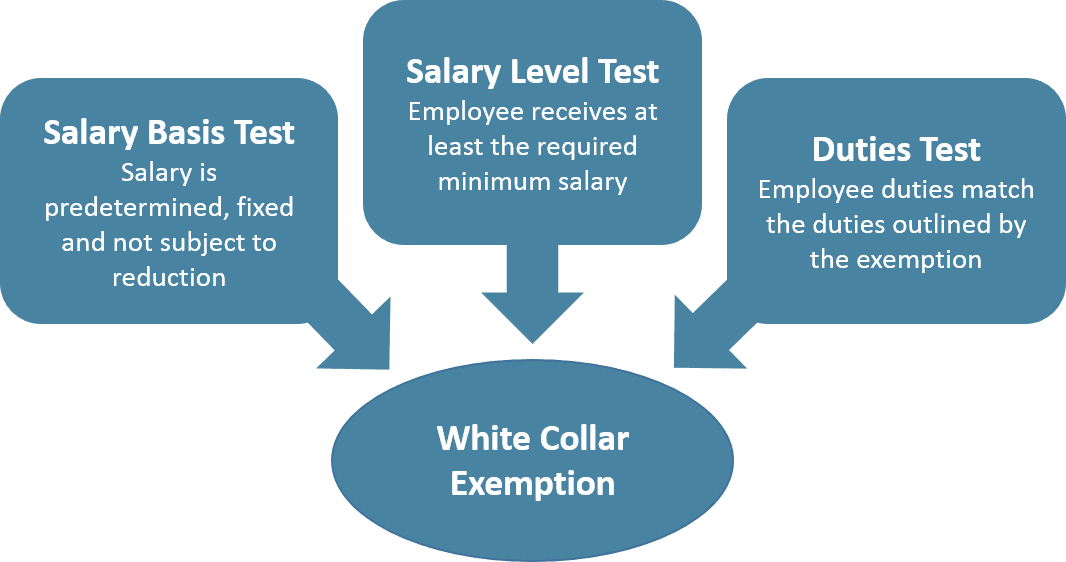
To qualify for a white collar exemption, an employee must meet a salary basis test, a salary level test and a duties test. Job titles or salary wages alone do not determine exempt status.
- The salary basis test is used to make sure the employee is paid a predetermined and fixed salary that is not subject to reduction due to variations in the quality or quantity of work.
- The salary level test is used to ensure that the employee meets a minimum specified amount to qualify for the exemption. This salary threshold provides employers with an objective and efficient way to determine whether an employee qualifies for a white collar exemption. The current salary level is set at $455 per week ($23,660 per year) for EAP employees and $100,000 per year for highly compensated employees.
- The duties test requires that the employee’s job duties conform to EAP duties, as defined by law. This analysis requires a more thorough evaluation of whether an employee can be classified as an administrative, professional, outside sales, computer or highly compensated employee.
The white collar exemptions do not apply to:
- “Blue collar” workers who typically perform manual labor. Blue collar worker occupations include mechanics, plumbers, electricians, construction workers and assembly line workers;
- Law enforcement personnel – Police officers, detectives, deputy sheriffs, state troopers, highway patrol officers, investigators, inspectors, correctional officers, parole or probation officers, and park rangers;
- First responders – Firefighters, paramedics, emergency medical technicians, ambulance personnel and rescue workers; or
- Hazardous materials workers (and similar employees), regardless of rank or pay level, who perform work such as preventing, controlling or extinguishing fires.
Duties Test
To satisfy the duties test, an employee’s actual work responsibilities must match the description the FLSA assigns to each exemption. The table below presents an overview of the job descriptions assigned for each white collar exemption.
| Exemption Type | Duties and Qualifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Executive |
|
|
| Administrative |
|
|
| Creative Professional |
|
|
| Learned Professional |
|
|
| Computer Employee |
|
|
|
Outside Sales |
|
|
| Highly Compensated Employees |
|
|
This Compliance Overview is not intended to be exhaustive nor should any discussion or opinions be construed as legal advice.
Readers should contact legal counsel for legal advice.
© 2016-2017 Zywave, Inc. All rights reserved. JPA 9/17
Material posted on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a legal opinion or medical advice. Contact your legal representative or medical professional for information specific to your legal or medical needs.